Physical Examination
Upon examination, both acute and long-term use of methamphetamine can lead to abnormal findings in the following organ systems:
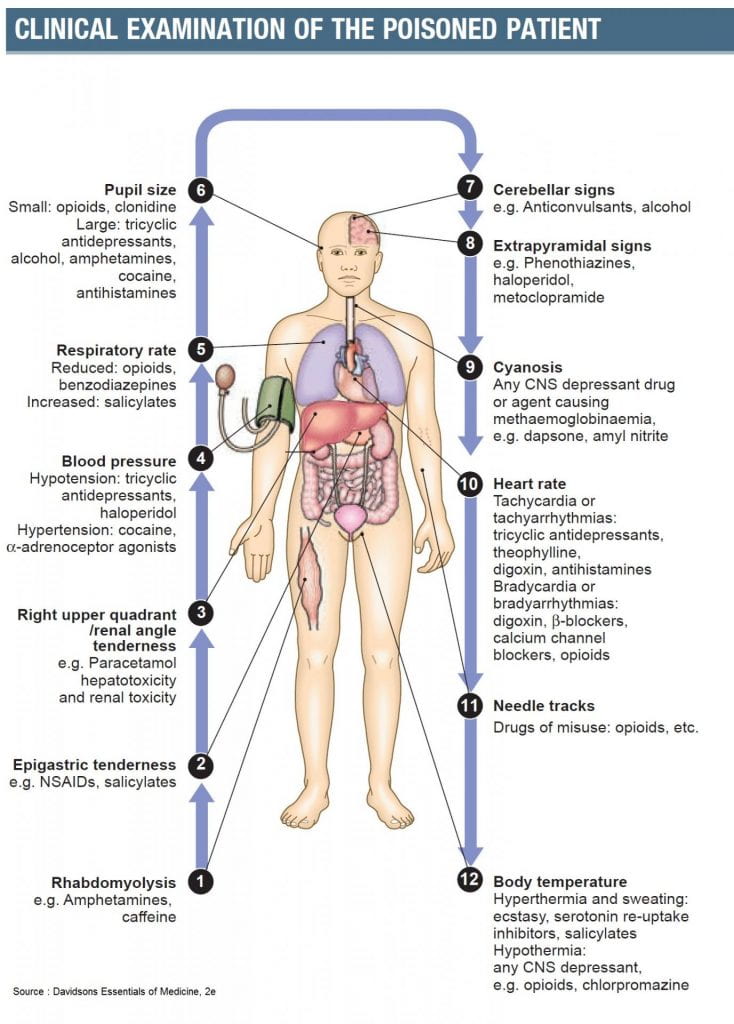
- Cardiovascular
- Central nervous system
- Gastrointestinal
- Renal
- Skin
- Dental
Cardiovascular findings are as follows
- Tachycardia and hypertension are both frequently observed
- Atrial and ventricular arrhythmias may occur
- Chest pain from myocardial ischemia and/or infarctions
- Acute use associated with aneurysms and aortic dissection
- Chronic use associated with accelerated atherosclerosis
- Hypotension can be observed in an overdose if significant depletion of catecholamines ensues
- Coma may also result from catecholamine storage depletion
Respiratory findings are as follows
- Barotrauma, such as pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, and pneumopericardium may occur from forceful inhalation
- Acute noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and pulmonary hypertension can result from both acute and chronic use
- Wheezing from reactive airway disease may be induced by methamphetamine
Gastrointestinal findings are as follows
- Hepatocellular damage may result in acute and chronic abuse. Direct effects originating from this impairment are:
- Hypotension
- Hepatoxic contaminants
- Lipid peroxidation
- Necrotizing angiitis
- Severe abdominal pain can occur from acute mesenteric vasoconstriction. Ischemic colitis may also transpire.
Renal failure associated with amphetamines is related to the following
- Hypoxemia
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Necrotizing angiitis
- Acute interstitial nephritis
- Cardiovascular shock with subsequent acute tubular necrosis
Skin findings include the following
- Delusions of parasitosis along with chronic skin-picking are often seen causing prurigo nodularis, also known as “speed bumps”
- Abscess and cellulitis are common for methamphetamine injectors
Dental examination findings
- Severe tooth decay, particularly of the maxillary teeth – upper jaw – is common in chronic meth users.
- This is also referred to as “meth mouth”
- This finding is the result of maxillary artery vasoconstriction, xerostomia, and poor hygiene.
Information gathered from:


